The terms ‘Lab-grown’, ‘CVD’ or ‘Synthetic’ Diamonds have rung over our ears for quite some time now.
The terms ‘Lab-grown’, ‘CVD’ or ‘Synthetic’ Diamonds have rung over our ears for quite some time now. We know that technology is prevailing new methods and techniques to replicate the natural process of diamond making to controlled environment in the lab. The question next is how are diamonds manufactured in lab and how it is done?
What are these diamonds?
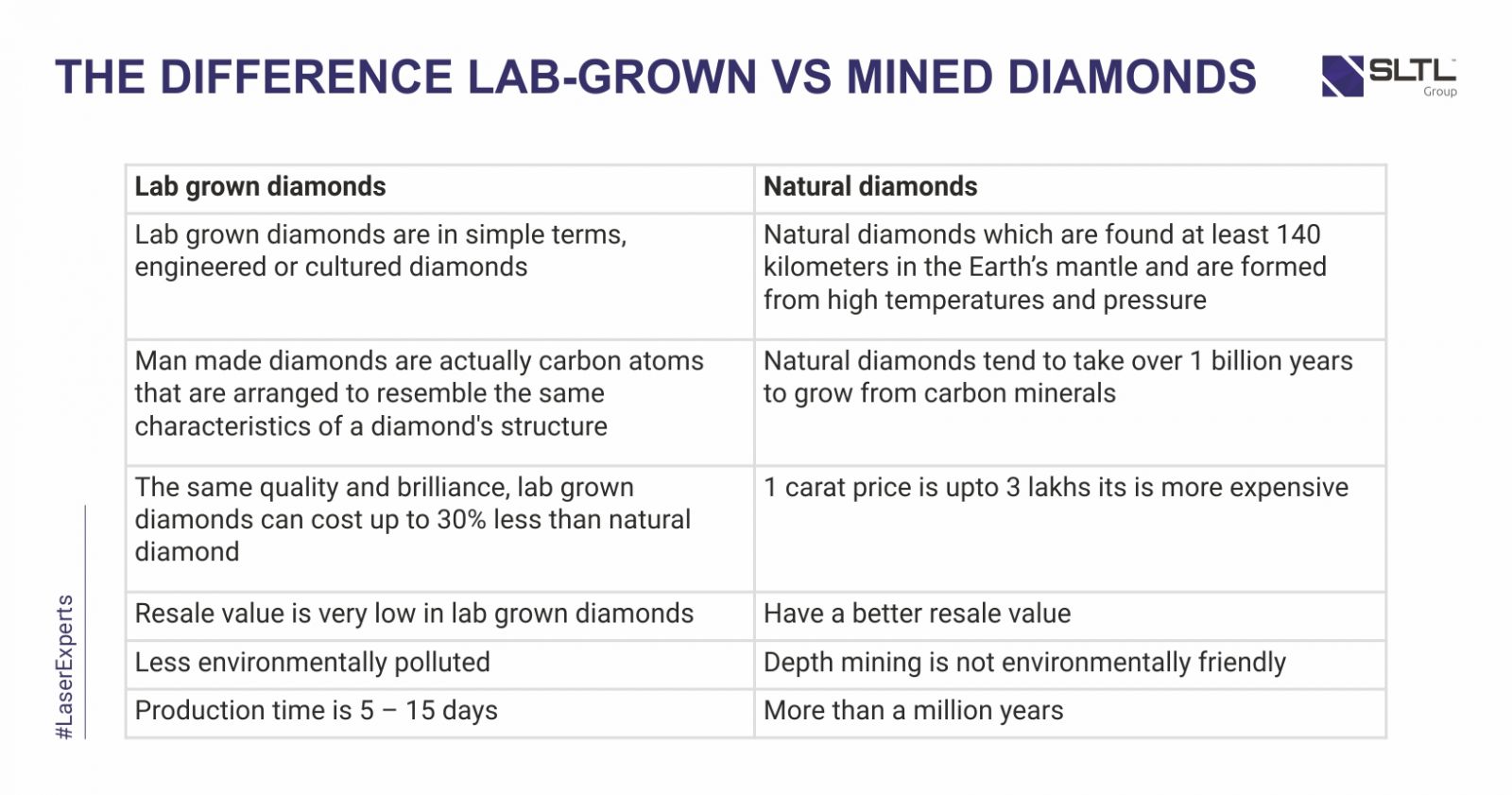
Lab-grown diamond unlike mined are grown under complete human regulatory conditions and observations. The only difference between Lab-grown Diamonds and naturally diamonds is the source of origin.
The only factor that makes a lab-created diamond totally different from a natural diamond is its origin. A science laboratory-created diamond is “grown” inside a lab using newest technology that replicates the natural diamond growing method. The results an artificial diamond that’s with chemicals, physically, and optically the same as those grown at a lower place the Earth’s surface.
How are they developed?
Geologists believe that natural diamonds are formed deep within the earth and are nearly 1 billion to 3.5 billion years old. These natural process of carbon melting and forming crystals is suitable processed at a depth of around 100 to 150 miles. These diamonds are exposed to the earth’s surface through volcanic eruptions.
Though the process of manufacturing Lab-grown diamond is different and far more quickly. There are mainly two methods which are deployed by the labs to manufacture Lab-grown diamonds:
1. HPHT Process
2. CVD Process
In a HPHT (High Pressure-High Temperature) process a small diamond seed is placed into carbon. The seed is then exposed at the bottom of a press to extreme high temperatures of around 1500 °C and pressure of 1.5 million pounds per area unit is applied. The pure carbon starts melting to form a diamond round around the starter seed. During this process extreme temperatures and pressures have likelihood to form a crack in the diamonds. Thus, extensive monitoring and examination has became an integral part of this process
CVD stands for Carbon Vaporized Deposition and this method in comparison to HPHT method is rather modern. The common practice is to put a slice of a diamond (as a starter seed) in a sealed chamber and heated to around 800 °C. The sealed chamber is filled with carbon rich gases like methane and others. The gases area unit is ionized into plasma exploitation technology similar to that of microwaves or lasers. The ionization breaks the molecular bonds within the gases, and also the pure carbon adheres to the diamond seed and slowly crystallize.
Comparing the methods.
The main advantage of CVD over HPHT process is that it does not need the temperatures and pressures as high as in HPHT. Even the CVD diamonds are inexpensive than that produced through HPHT because of low temperatures and pressures required by the CVD process. Adding to that, CVD diamonds can be grown over larger areas by starting with a larger diamond seed plate. This process allows for a finer control over the environment in the growth chamber resulting into the properties of the finished diamonds. Although, the largest known polished lab grown CVD diamond is only 3.23 carats graded as I color and VS2 clarity.